

Last modified: 2006-07-08 by antonio martins
Keywords: semaphore | oscar |
Links: FOTW homepage |
search |
disclaimer and copyright |
write us |
mirrors
“Flag language”, or “semaphore” — a
convention to convey (latin) letters by means of two flaglets, held in
each hand, and several positions of both arms.
This is not a “language”, of course, rather an “alphabet”
(the same way Morse or Braille are alphabets — they’re
actually cyphers).
António Martins, 27 Jul 2003 and 07 May 2005
As a noun the word "semaphore" (from the Greek
"σημια", "sign", and
"φορος", "bearing") is the name given
to the system of sending messages by holding the arms, two poles
or two flags in certain positons according to an alphabetic code,
or a mechanical device for signalling in the same way. As a
verb it means «to signal in by these means».
The person who does the “semaphoring” is a
signaller.
Christopher Southworth, 27 Jul 2003
Nautical signal and semaphore flags, storm
flags, I suggest, are a special sort of occasional flag
Bill Dunning, 29 Aug 2003
There is no symbolism on these semaphore “flags”,
which may be a colored paddle.
Albert Kirsch, 31 Aug 2003
The actual flags used were (and are) entirely irrelevant
to the system.
Christopher Southworth, 27 Jul 2003
What gives semaphore flags content is not their design
at all, but rather their position! A signalman without
flags could still just wave his arms and get his message
across; the “flags” just add visibility.
Albert Kirsch, 29 Aug 2003
Question: What colour flag should I use for semaphore
signalling.
Answer: The design is irrelevant.
Dean McGee, 28 Jul 2003
Did the Armies of the various countries in Europe and the USA use
different and distinctive patterns for the semaphore flags
of their artillery corps?
At the Suffolk Regimental Museum in Bury-St Edmunds, in Britain,
former colleague of mine was shown a flag picked up by a member of the
regiment on the battlefield of Paardeberg (Feb 17 to Feb 27 1900 -
Anglo-Boer War): It was a square red flag with a white square at the
centre. At the Artillwry section of the War Museum of the Boer
Republics in Bloemfontein, South Africa, former capital of the Orange
Free state Republic, the curator identified it as a semaphore flag of
the OFS State Artillery. He also told me that
the same design was the used by the British
Royal Artillery. He had another semaphore flag, white with a narrow
blue cross, in his collection which was used for semaphore signalling
by the ZAR (Transvaal) State Artillery. This
was apparently the pattern used by the German
Army’s artillery corps.
Andre Burgers, 04 Apr 2005
US Army used red with a white rectangle
(when signaling with a light colored background behind the sender) or
white with a red rectangle (when the background was dark).
US Navy uses (still) the
ICS OSCAR flag, divided diagonally yellow
and red.
I seem to recall that the [British] Royal Navy
once used a horizontally triband, either white-blue-white or
blue-white-blue depending on background, but may be mistaken.
Joe McMillan, 01 Jul 2003
In the South African Navy and, I believe the
British Royal Navy and possibly also throughout
NATO, the semaphore signal flags were square
Flags OSCAR, presumably because the
red and yellow diagonal design had high visibility at sea.
Andre Burgers, 28 Jul 2003
I had seen the red/white US Army flags in
the 1917 Nat’l Geo [gmc17].
And I remembered seeing a badge from a Canadian
Forces signal unit that included crossed blue/white flags. I found
a couple of examples like this site in
Canadian,
Australian, and
British Army units.
The symbol is a white-blue-white triband crossed with a
plain blue flag.
And this site
seems to show the plain blue flag in use in the Zulu war,
1879 (but the pic is small: it may be a regimental flag or some
such).
Dean McGee, 01 Aug 2003
From a book called The schoolboy’s Pocket Book by Carlton Wallace (first published in the 1950s):
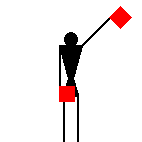
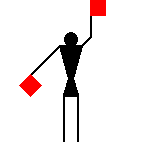
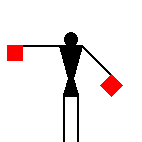
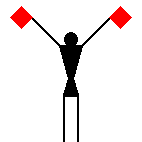
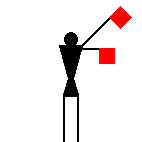
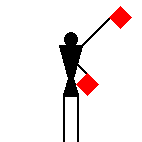
James Dignan, 07 Jun 2005Before a semaphore transmission begins, it is usual to hoist the letters VOX [victor oscar x-ray] or simply J [juliet] in the International Code flags from a convenient flagstaff.
The signaller then gives the Semaphore alphabetical sign (identical to the signal for the letter J) and waits until the person receiving the message replies with the letter C.
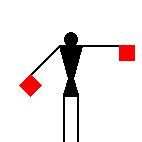
If numbers are to be sent, the signaller makes the numerical sign; he makes the alphabetical sign again when going back to ordinary letters.
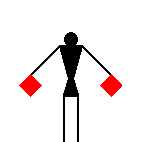
When receiving, the signaller stands at the “ready” position with the two flags crossed in front of the legs.





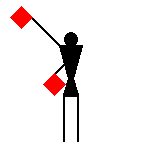
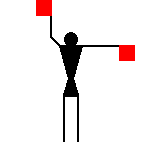

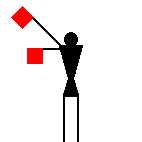
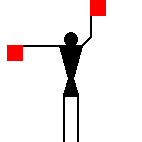
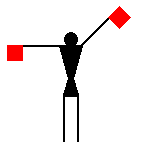
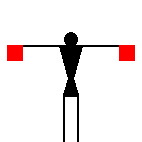


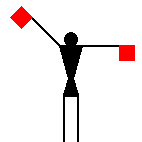




The peace symbol originated from
semaphore for "N" (the two diagonal lines) and
"D" (the two vertical lines). Later the symbol was adopted as a
general peace sign.
T.F. Mills, 09 Oct 1996







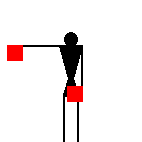
Zero is the same combination as letter K.
James Dignan, 07 May 2005



The peace symbol originated
from semaphore for "N" (the two diagonal lines) and
"D" (the two vertical lines).
Later the symbol was adopted as a general peace sign.
T.F. Mills, 09 Oct 1996













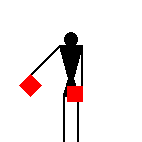
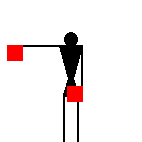

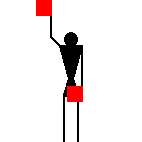
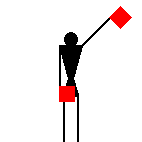
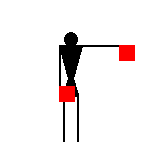
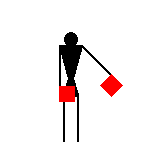
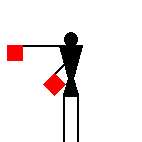
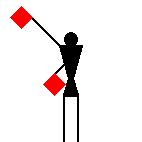
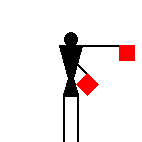
The number signals are identical to ten of the letters.
James Dignan, 07 May 2005

Zero is the same combination as letter K.
James Dignan, 07 May 2005









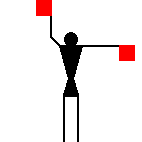
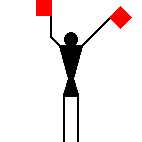
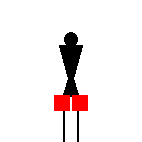

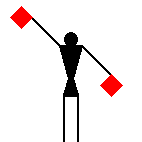

As far as I know, there are no punctuation marks in the
system.
Terence Martin, 06 May 2005

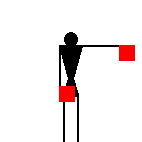
The signaller makes the alphabetical sign when going back to
ordinary letters, after having sent
numbers (introduced by the numerical
sign). The Semaphore alphabetical sign is
identical to the signal for the letter J.
James Dignan, 07 Jun 2005

If numbers are to be sent the signaller makes
the numerical sign; he makes the alphabetical sign
again when going back to ordinary letters.
James Dignan, 07 Jun 2005
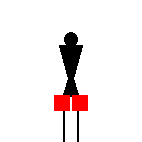
When receiving, the signaller stands at the
“ready” position
with the two flags crossed in front of the legs.
This signal may have been used for breaks between words.
James Dignan, 07 Jun 2005

The person receiving the message must acknowledge, before start,
with the letter C.
James Dignan, 07 Jun 2005

This flag means «correction»; it is sent following any mistaken
signal.
James Dignan, 07 Jun 2005

Anything below this line was not added by the editor of this page.