![[Third Reich 1933-1945 (Germany)]](../images/d/de~1933.gif) 3:5
3:5 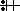
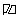
by Mark Sensen and António Martins
Flag adopted March 1933 as co-national flag, September 1935 as national flag

Last modified: 2005-10-01 by santiago dotor
Keywords: third reich | nationalsocialist | disc (white) | swastika (black) | cross: swastika (black) | hakenkreuz |
Links: FOTW homepage |
search |
disclaimer and copyright |
write us |
mirrors
![[Third Reich 1933-1945 (Germany)]](../images/d/de~1933.gif) 3:5
3:5 
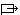
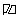
by Mark Sensen and António Martins
Flag adopted March 1933 as co-national flag, September 1935 as national flag
See also:
Other sites:
The second period of Nazi era flags starts late in the year 1935. The popular mythology ascribes this to an incident which occurred in New York on 26 July 1935 in which a group of (allegedly Communist) demonstrators attacked the German liner Bremen and threw its Swastika flag in the river. When the German charge d'affaires protested to the State Department, among the comments allegedly made, was that the national flag had not been interfered with, but only the party flag. Personally, I doubt the importance of the incident in German flag history and prefer the explanation which notes that by 1935, [President von] Hindenburg was dead, the Army had come to terms with the Nazis and the German Nationals [Party] had ceased to be an important political factor.
In any event, in 1935 the Nazis again changed almost all of the German flags, specifically:
Norman Martin, January 1998
On the 5th October 1935 some flags were adopted:
Pascal Vagnat, 14 June 1998
From Flagmaster [flm] no. 078:
The Nazi flag laws [were] the Law for the Protection of the National Symbols of 19 May 1933, and the Reich Flag Law [Reichsflaggengesetz] of 15th September 1935 (the Nuremberg Flag Law). (...) The Law for the Protection of the National Symbols had given powers to Goebbels as Reich Minister of Enlightenment and Propaganda to control flag usage, and the Reich Flag Law made the use of the national symbols more specific, established the swastika as the national flag and allowed for a new Reichskriegsflagge.
Mark Sensen, 14 January 1997
![[Civil Flag 1935-1945 (Third Reich, Germany)]](../images/d/de-1933.gif) 3:5
3:5 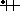
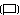
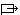
![[Civil Ensign 1935-1945 (Third Reich, Germany)]](../images/d/de~1933.gif) 3:5
3:5 
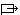
both by Mark Sensen and António Martins
This flag is unchanged from [the] 1933 swastika flag and became the national and merchant flag, replacing the black-white-red tricolor. The same pattern was also used as jack, replacing the 1933 jack. This can be found in countless books, the best for exactness being Flaggenbuch 1939 [neu39], plate II under Deutsches Reich, which contains exact proportions. As the merchant flag and jack, the white disk was placed somewhat closer to the hoist.
Norman Martin, January 1998